How to extract Git statistics from git repositories

Here in this article we will try to implement a python flask application to get GitHub repository git statistics by leveraging gitstats utility.
What is GitStats
gitstats is utility that helps in generating statistics from git repositories. It provides developers with useful information on the activities that are carried out within a particular git repositories by multiple developers. Currently it only supports generating the output in HTML format with tables and graphs.
GitStats Features
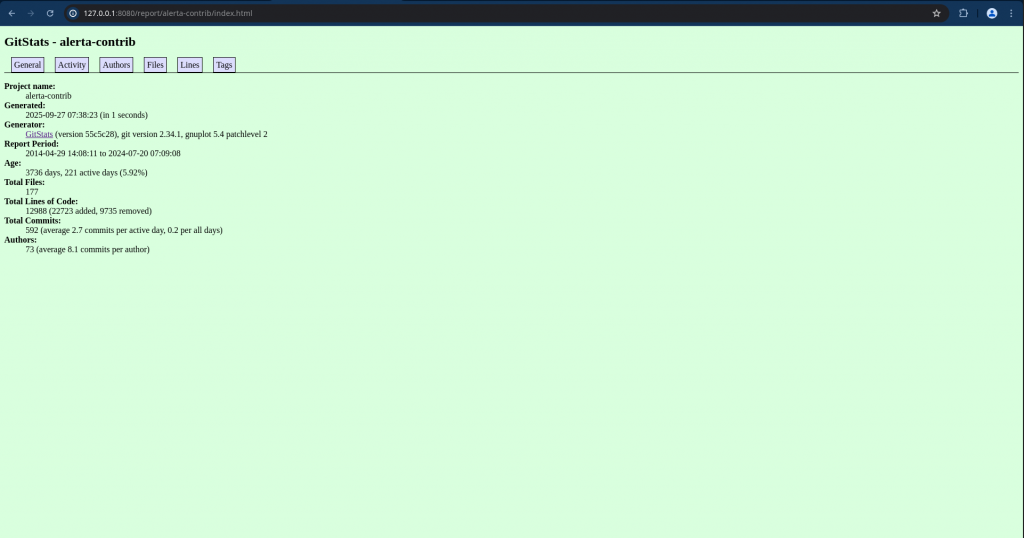
- General statistics: total files, lines, commits, authors.
- Activity: commits by hour of day, day of week, hour of week, month of year, year and month, and year.
- Authors: list of authors (name, commits (%), first commit date, last commit date, age), author of month, author of year.
- Files: file count by date, extensions
- Lines: Lines of Code by date
Currently GitHub or GitLab provides with contribution chart which is a visual representation on a user’s GitHub or GitLab profile page that displays their activity and contributions to repositories over the past year. It appears as a grid of colored squares, where each square represents a day and its color intensity indicates the level of contribution on that specific day as shown below.
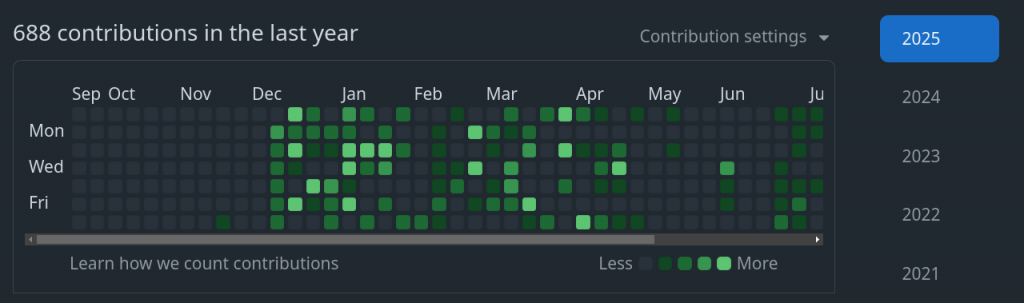
But GitHub or GitLab does not provide an out of the box visualization of statistics per project or repository. So here in this demo we will try to leverage GitHub repository ie. gitstats to achieve the same.
If you are interested in watching the video. Here is the YouTube video on the same step by step procedure outlined below.
Procedure
Step1: Ensure Docker installed
As we are going to implement a python flask application and run it as docker container, we need to ensure that docker is installed on the machine.
admin@fedser:gitstats$ sudo systemctl status docker.service
Step2: Create a requirements.txt file
Let’s create a python requirements.txt file to install the necessary dependency needed to run the application.
admin@fedser:gitstats$ cat requirements.txt
flask
requests
Step3: Create Python Flask Application
Here is a very basic python flask application which runs with python3 runtime. It does the following tasks.
- repos: Gets the list of repositories for a particular user profile in GitHub
- clone: Clones the GitHub repository locally within the docker container in a temp location
- gitstats_report: Leverages gitstats utility to generate statistics report for the git repository cloned locally
- get_report_file: Provides an endpoint to access the HTML report for the repository
admin@fedser:gitstats$ cat app.py
import os
import subprocess
import tempfile
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, send_file
from flask import send_from_directory
app = Flask(__name__)
BASE_CLONE_DIR = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), "cloned_repos")
BASE_REPORT_DIR = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), "gitstats_reports")
os.makedirs(BASE_CLONE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(BASE_REPORT_DIR, exist_ok=True)
def get_repos(user):
# Use GitHub API to get public repos for a user
import requests
url = f"https://api.github.com/users/{user}/repos"
resp = requests.get(url)
repos = [{"name": r["name"], "clone_url": r["clone_url"]} for r in resp.json()]
return repos
def clone_repo(clone_url, repo_name):
repo_dir = os.path.join(BASE_CLONE_DIR, repo_name)
if os.path.exists(repo_dir):
return repo_dir
subprocess.check_call(["git", "clone", clone_url, repo_dir])
return repo_dir
def run_gitstats(repo_dir, report_dir):
# Assumes gitstats is installed and available in PATH
subprocess.check_call(["gitstats", repo_dir, report_dir])
@app.route("/repos/<username>", methods=["GET"])
def repos(username):
repos = get_repos(username)
return jsonify(repos)
@app.route("/clone", methods=["POST"])
def clone():
data = request.json
clone_url = data.get("clone_url")
repo_name = data.get("repo_name")
if not clone_url or not repo_name:
return jsonify({"error": "clone_url and repo_name required"}), 400
try:
repo_dir = clone_repo(clone_url, repo_name)
return jsonify({"repo_dir": repo_dir})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 500
@app.route("/gitstats", methods=["POST"])
def gitstats_report():
data = request.json
repo_name = data.get("repo_name")
if not repo_name:
return jsonify({"error": "repo_name required"}), 400
repo_dir = os.path.join(BASE_CLONE_DIR, repo_name)
report_dir = os.path.join(BASE_REPORT_DIR, repo_name)
try:
run_gitstats(repo_dir, report_dir)
return jsonify({"report_url": f"/report/{repo_name}"})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 500
@app.route("/report/<repo_name>/<path:filename>", methods=["GET"])
def get_report_file(repo_name, filename):
report_dir = os.path.join(BASE_REPORT_DIR, repo_name)
# if not filename.endswith('.html'):
# return jsonify({"error": "Only .html files are allowed"}), 400
file_path = os.path.join(report_dir, filename)
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
return jsonify({"error": "Report file not found"}), 404
return send_from_directory(report_dir, filename)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#app.run(debug=True)
app.run(debug=True, host='0.0.0.0', port=8080)
NOTE: Flask application is listening on port 8080 within container
Step4: Create Dockerfile
Here we are preparing a Dockerfile, which uses a base image “ubuntu:22.04” on top of which we are installing the necessary dependencies such as “git, python3, pip, curl, make” required for python flask application and “python2, gnuplot, make and perl” required for the gitstats utility to run.
Once the necessary dependencies are installed, we are copying the flask application files “app.py and requirements.txt” to docker container and exposing the application on host port 8080 to map to container port 8080 where the flask application is getting launched.
admin@fedser:gitstats$ cat Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:22.04
# Install dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
git \
python3 \
python3-pip \
python2 \
curl \
gnuplot \
make \
perl \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Create directory structures
RUN mkdir /app /usr/local/share/gitstats
# Clone gitstats repository
RUN git clone https://github.com/hoxu/gitstats.git /opt/gitstats
# Build and install gitstats
WORKDIR /opt/gitstats
RUN make install
# Copy flask application
COPY app.py requirements.txt /app
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install python dependencies
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
# Expose application on port 8080
EXPOSE 8080
# Run application
ENTRYPOINT [ "/usr/bin/python3" ]
CMD [ "app.py" ]
Step5: Create an API testing file
Here let’s create a .http file a plain text file used to define and execute HTTP requests, primarily for testing and interacting with API endpoints directly within an Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
admin@fedser:gitstats$ cat gitstats.http
### Get List of repositories
GET http://127.0.0.1:8080/repos/novicejava1
### Clone a repository
POST http://127.0.0.1:8080/clone
Content-Type: application/json
{
"repo_name": "alerta-contrib",
"clone_url": "https://github.com/novicejava1/alerta-contrib.git"
}
### Generate gitstats for repository
POST http://127.0.0.1:8080/gitstats
Content-Type: application/json
{
"repo_name": "alerta-contrib"
}
### Validate gitstats report for repository
GET http://127.0.0.1:8080/report/alerta-contrib/index.html
Step6: Build Docker Image
Once we are ready with our code and dockerfile, we can build our docker image as shown below.
admin@fedser:gitstats$ docker build -t gitstats:0.0.1 .
Step7: Run Docker Container
It’s time to run our docker contianer using the image that we build in our previous step.
admin@fedser:gitstats$ docker run -d -p 8080:8080 --name gitstats gitstats:0.0.1
Step8: Validate GitStats
Run the “gitstats.http” testcase file within your IDE and check the results. For vscode you need to install the restclient extension to work with .http files.
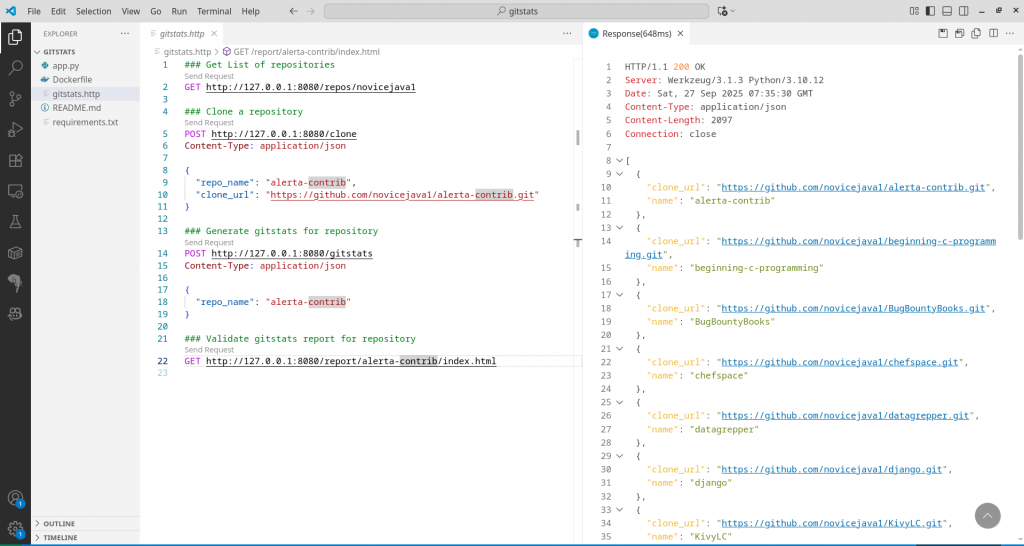
List the repositories for a GitHub profile
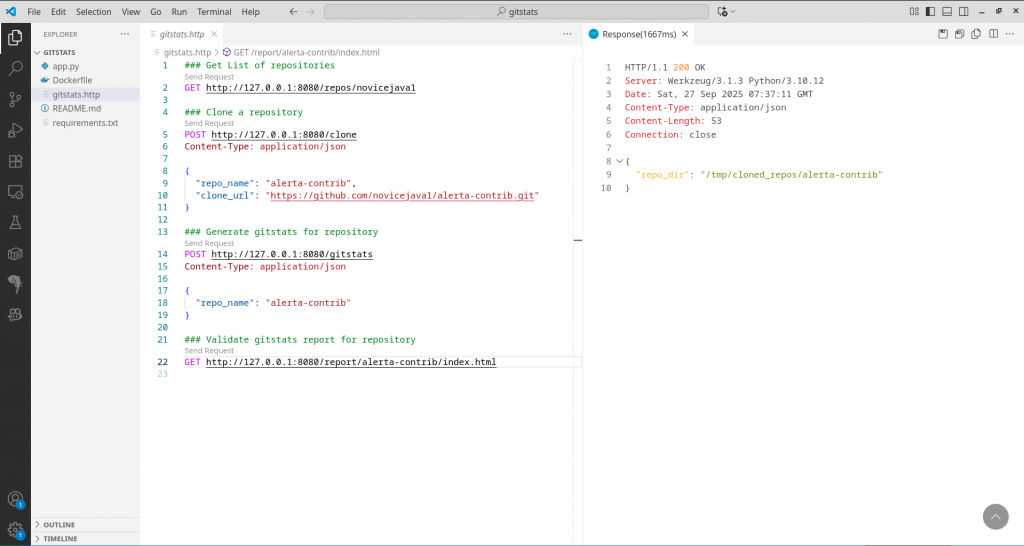
Clone the repository
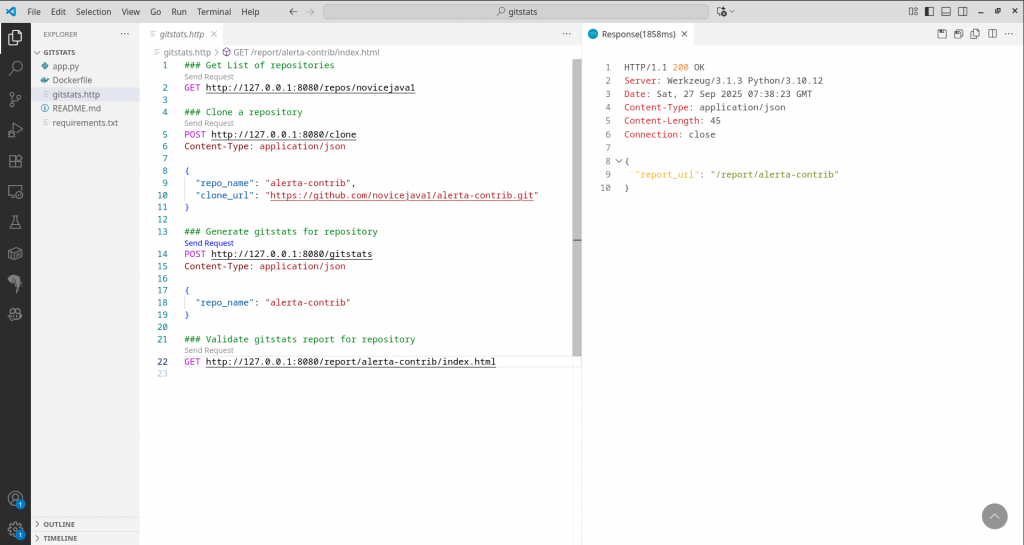
Generate git statistics
Validate gitstats report
Hope you enjoyed reading this article. Thank you..
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.