How to build and deploy event driven application using knative

Here in this article we will try to build and deploy an event driven application using knative.
Test Environment
- Knative v1.19.4
What is Knative Eventing
Knative Eventing is a set of APIs within the Knative project that enables the creation of event-driven architectures with applications running on Kubernetes. It provides the infrastructure to route events from various sources to different sinks (event consumers) in a loosely coupled manner.
Knative Eventing uses standard HTTP POST requests to send and receive events between event producers and sinks. These events conform to the CloudEvents specifications, which enables creating, parsing, sending, and receiving events in any programming language.
High Level Architecture
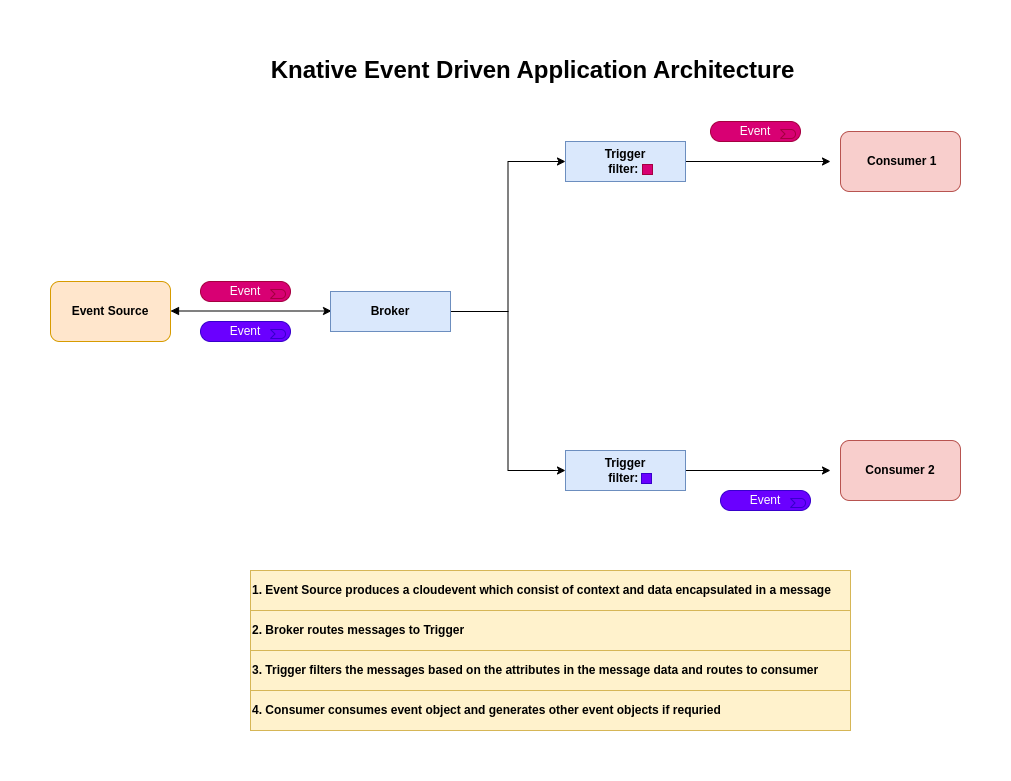
If you are interested in watching the video. Here is the YouTube video on the same step by step procedure outlined below.
Procedure
Step1: Ensure Kubernetes cluster with Knative installed
Follow my blog on “How to build and deploy serverless application using Knative” to setup a local kubernetes cluster using kind and install the knative quickstart plugin to setup knative platform on top kubernetes cluster.
Step2: Create a Python flask based web server application
Here let’s create a basic python flask application which accepts a POST request and responds back with a message and set of headers related to cloudevents.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ cat helloworld.py
from flask import Flask, request, make_response
import uuid
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', methods=['POST'])
def hello_world():
app.logger.warning(request.data)
# Respond with another event (optional)
response = make_response({
"msg": "Hi from helloworld-python app!"
})
response.headers["Ce-Id"] = str(uuid.uuid4())
response.headers["Ce-specversion"] = "0.3"
response.headers["Ce-Source"] = "knative/eventing/samples/hello-world"
response.headers["Ce-Type"] = "dev.knative.samples.hifromknative"
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, host='0.0.0.0', port=8080)
Step3: Dockerize Flask application
Once you python flask application is ready we can dockerize it using the Dockerfile as shown below and push the image to DockerHub.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ cat Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9-alpine
COPY . /app
WORKDIR /app
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT [ "python" ]
CMD [ "helloworld.py" ]hellopython-00001-deployment-7cbf8cdcc5-9mv27
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ docker build -t docker.io/novicejava1/hellopython:latest .
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ docker push novicejava1/hellopython:latest
Step4: Deploy Flask application using knative
Let’s now create a namespace “eventing” with eventing enabled.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ cat ns.yml
# Namespace for sample application with eventing enabled
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: eventing
labels:
eventing.knative.dev/injection: enabled
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kubectl apply -f ns.yml
namespace/eventing created
Now, let’s create a service.yml file to deploy the python flask application as service into knative cluster. Once the service.yml file is created we can apply it to the knative cluster.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn service create hellopython --image novicejava1/hellopython:latest --target=/home/admin/eventingdemo/service.yml -n eventing
Service 'hellopython' created in namespace 'eventing'.
admin@linuxscratch:~/eventingdemo$ kubectl apply -f service.yml
Warning: Kubernetes default value is insecure, Knative may default this to secure in a future release: spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation, spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.capabilities, spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.runAsNonRoot, spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.seccompProfile
service.serving.knative.dev/hellopython created
We will now be able to see our service deployed to “eventing” namespace as shown below and exposed at the endpoint mentioned in the URL section. This service deployment also creates a route and revision as shown below.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing service list
NAME URL LATEST AGE CONDITIONS READY REASON
hellopython http://hellopython.eventing.127.0.0.1.sslip.io hellopython-00001 54s 3 OK / 3 True
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing route list
NAME URL READY
hellopython http://hellopython.eventing.127.0.0.1.sslip.io True
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing revision list
NAME SERVICE TRAFFIC TAGS GENERATION AGE CONDITIONS READY REASON
hellopython-00001 hellopython 100% 1 90s 3 OK / 4 True 1 3m28s 3 OK / 4 True
Let’s create a Broker in eventing namespace with Broker class as MTChannelBasedBroker.
An MTChannelBasedBroker is a Knative Eventing component that routes events by using underlying channels, and an InMemoryChannel is the default, in-memory channel implementation for this broker. Together, the MTChannelBasedBroker with InMemoryChannel provides a basic, non-durable event routing mechanism, making it suitable for local development and testing but not recommended for production due to its lack of persistence and message recovery capabilities.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn broker create pythonbroker --namespace eventing --class MTChannelBasedBroker
Broker 'pythonbroker' successfully created in namespace 'eventing'.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing broker list
NAME URL AGE CONDITIONS READY REASON
pythonbroker http://broker-ingress.knative-eventing.svc.cluster.local/eventing/pythonbroker 44s 7 OK / 7 True
Step5: Create a trigger
A Knative Trigger is a Knative Eventing resource that acts as a filter, subscribing to events from a Broker and forwarding them to a specified Sink (like a Knative service) based on CloudEvents attributes.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing trigger create pythontrigger --broker pythonbroker --filter type=dev.knative.samples.hellopython --sink ksvc:hellopython
Trigger 'pythontrigger' successfully created in namespace 'eventing'.
Step6: Generate cloudevent for broker
Now that we have our service deployed along with default broker channel and trigger implementation in place, we can send a cloudevent message to broker with Ce-Type as “dev.knative.samples.hellopython”. CloudEvents messages with this type gets filtered by the trigger and are routed to the hellopython service deployed in the knative cluster.
admin@linuxser:~$ kubectl -n eventing run -it --rm curl-test --image=curlimages/curl:latest -- /bin/sh
Once you are in the interactive shell terminal for the curlimage, trigger an HTTP POST request using the below.
curl -v "broker-ingress.knative-eventing.svc.cluster.local/eventing/pythonbroker" \
-X POST \
-H "Ce-Id: 536808d3-88be-4077-9d7a-a3f162705f79" \
-H "Ce-specversion: 0.3" \
-H "Ce-Type: dev.knative.samples.hellopython" \
-H "Ce-Source: dev.knative.samples/helloworldsource" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"msg":"Message for hellopython app from the curl pod."}'
Step7: Verify Cloudevent on Flask Application side
We can verify the logs of the pods that are instantiated when a request is received as shown below. This python application further sends a response but currently we do not have subscriber ready to receive those messages so the message gets lost with the default implementation.
admin@linuxser:~/pythoeventingdemo$ kubectl -n eventing logs hellopython-00001-deployment-6579b7c7d4-bnvmw
* Serving Flask app 'helloworld'
* Debug mode: on
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:8080
* Running on http://10.244.0.33:8080
Press CTRL+C to quit
* Restarting with stat
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 678-418-799
[2025-09-15 10:31:59,262] WARNING in helloworld: b'{"msg":"Message for hellopython app from the curl pod."}'
127.0.0.1 - - [15/Sep/2025 10:31:59] "POST / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
[2025-09-15 10:32:05,639] WARNING in helloworld: b'{"msg":"Message for hellopython app from the curl pod."}'
127.0.0.1 - - [15/Sep/2025 10:32:05] "POST / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
[2025-09-15 10:32:07,682] WARNING in helloworld: b'{"msg":"Message for hellopython app from the curl pod."}'
127.0.0.1 - - [15/Sep/2025 10:32:07] "POST / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
Step8: Create a Sink Service
Let’s now create a sink service “event-display” which can be used to display the cloudevent messages.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn service create event-display --image gcr.io/knative-releases/knative.dev/eventing/cmd/event_display --target=/home/admin/eventingdemo/event-display.yml -n eventing
Service 'event-display' created in namespace 'eventing'.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kubectl apply -f event-display.yml
Warning: Kubernetes default value is insecure, Knative may default this to secure in a future release: spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.allowPrivilegeEscalation, spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.capabilities, spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.runAsNonRoot, spec.template.spec.containers[0].securityContext.seccompProfile
service.serving.knative.dev/event-display created
Now if we list the services, we have both “hellopython” and “event-display” service deployed.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing service list
NAME URL LATEST AGE CONDITIONS READY REASON
event-display http://event-display.eventing.127.0.0.1.sslip.io event-display-00001 60s 3 OK / 3 True
hellopython http://hellopython.eventing.127.0.0.1.sslip.io hellopython-00001 15m 3 OK / 3 True
Step9: Create a Trigger deliver the event to the previously created service
Let’s now create another trigger that routes cloudevents messages to “event-display” service when the type is “dev.knative.samples.hifromknative” as shown below.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kn -n eventing trigger create event-display --broker pythonbroker --filter type=dev.knative.samples.hifromknative --sink ksvc:event-display
Trigger 'event-display' successfully created in namespace 'eventing'.
Step10: Verify events received by the event-display pods
Try to send some messages from the curl pod as done in Step5 and tail the logs for both the hellopython and event-display to see the events getting received and responded.
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kubectl -n eventing logs hellopython-00001-deployment-6579b7c7d4-zrg9c
* Serving Flask app 'helloworld'
* Debug mode: on
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment. Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:8080
* Running on http://10.244.0.35:8080
Press CTRL+C to quit
* Restarting with stat
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 367-326-198
[2025-09-15 10:44:04,266] WARNING in helloworld: b'{"msg":"Message for hellopython app from the curl pod."}'
127.0.0.1 - - [15/Sep/2025 10:44:04] "POST / HTTP/1.1" 200 -
admin@linuxser:~/eventingdemo$ kubectl -n eventing logs event-display-00001-deployment-df4997d58-w4dg6
2025/09/15 10:44:05 failed to parse observability config from env, falling back to default config
2025/09/15 10:44:05 failed to correctly initialize otel resource, resouce may be missing some attributes: the environment variable "SYSTEM_NAMESPACE" is not set, not adding "k8s.namespace.name" to otel attributes
☁️ cloudevents.Event
Context Attributes,
specversion: 0.3
type: dev.knative.samples.hifromknative
source: knative/eventing/samples/hello-world
id: e2ba7a07-d145-4703-b4d6-9a62713180d1
datacontenttype: application/json
Extensions,
knativearrivaltime: 2025-09-15T10:44:04.270460448Z
Data,
{
"msg": "Hi from helloworld-python app!"
}
Hope you enjoyed reading this article. Thank you..
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.