How to install and setup Docker Desktop on Fedora 35 workstation

Here in this article we will see how we can setup Docker Desktop on Fedora 35 workstation. We will first get a Docker Overview and proceed with the requirements for the Docker Desktop installation and them proceed with the setup for install Docker Desktop.
Test Environment
Fedora 35 workstation
What is Docker
Docker the most loved tool as per the Stack Overflow 2022 Developer Survey is used to build, ship and run your code or application packaged as a container irrespective of the infrastructure on which it is run. The containers build locally on a developer desktop machine can be run anywhere either locally, in cloud provider environment or a hybrid environment of both without any change. This increases the developer productivity so they just focus on building their application and also reduces the delivery time to the production environment or end user as its the same container that is going to be deployed in any environment.
Docker is written in the Go programming language and takes advantage of several features of the Linux kernel to deliver its functionality. Docker uses the concept of namespaces in linux which is used to build an isolated environment for a process in this case for a container. It creates a separate namespace for each container so they are isolated from each other.
Benefits of Docker
- Build portable application for fast and consistent delivery
- Scale the deployed application with ease as per business requirement
- Integrate with CICD pipeline for continuous build, deployment and testing of containerized application
Docker Architecture
Docker uses a client server architecture in which the docker client talks to the docker daemon which does the actual work of managing the images, containers, volumes and networks. Docker client and daemon can run on the same machine or you can connect docker client to a remote docker daemon. Docker client and daemon both communicate using REST API, over UNIX sockets or a network interface. Docker compose is another client that we can use to run multiple dependent containers as a service (ie. an application with postgres db requirement).
Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop is a collection Docker daemon (dockerd), Docker client (docker), Docker Compose (docker-compose), Docker Content Trust, Kubernetes and Credential Help components.
NOTE: Commercial use of Docker Desktop in larger enterprises (more than 250 employees OR more than $10 million USD in annual revenue) requires a paid subscription.
Docker Desktop System Requirements
Make sure the following requirements are met.
64 bit kernel with CPU supporting virtualization
uname -a
Output:
Linux feddocker.stack.com 5.14.10-300.fc35.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Oct 7 20:48:44 UTC 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
KVM virtualization support
lsmod | grep kvm
Output:
kvm_intel 331776 0
kvm 1019904 1 kvm_intel
irqbypass 16384 1 kvm
Add the user to group kvm as shown below.
sudo usermod -aG kvm $USER
Log out and log back in so that your group membership is re-evaluated.
QEMU must be version 5.2 or newer
/usr/bin/qemu-system-x86_64 --version
Output:
QEMU emulator version 6.1.0 (qemu-6.1.0-5.fc35)
Copyright (c) 2003-2021 Fabrice Bellard and the QEMU Project developers
systemd init system
Fedora by default supports systemd for service management.
Gnome or KDE Desktop environment
I am using a Fedora 35 workstation with GNOME support.
Memory requirements
Have atleast 4GB RAM
Enable configuring ID mapping in user namespaces
Docker Desktop relies on the host being configured to enable the current user to use subordinate ID delegation. For this to be true /etc/subuid (see subuid(5)) and /etc/subgid (see subgid(5)) must be present.
cat /etc/subuid
admin:100000:65536
cat /etc/subgid
admin:100000:65536
NOTE: Docker Desktop for Linux and Docker Engine can be installed side-by-side on the same machine. But it is recommended to stop the Docker Engine while you’re using Docker Desktop to prevent the Docker Engine from consuming resources and to prevent conflicts.
Procedure
Step1: Setup RPM Package repository
sudo dnf -y install dnf-plugins-core
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo
Step2: Download Docker Desktop
Download latest stable version of Docker Desktop from HERE.
Step3: Install Docker Desktop
sudo dnf install ./docker-desktop-4.11.0-x86_64.rpm
There are a few post-install configuration steps done through the post-install script contained in the RPM package.
The post-install script:
- Sets the capability on the Docker Desktop binary to map privileged ports and set resource limits.
- Adds a DNS name for Kubernetes to /etc/hosts.
- Creates a link from /usr/bin/docker to /usr/local/bin/com.docker.cli.
$ cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
# Added by Docker Desktop
# To allow the same kube context to work on the host and the container:
127.0.0.1 kubernetes.docker.internal
$ ls -ltr /usr/local/bin/com.docker.cli
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 15 Sep 8 15:06 /usr/local/bin/com.docker.cli -> /usr/bin/docker
Step4: Start Docker Desktop from GUI
Search for Docker Desktop in Fedora Applications list and launch it.
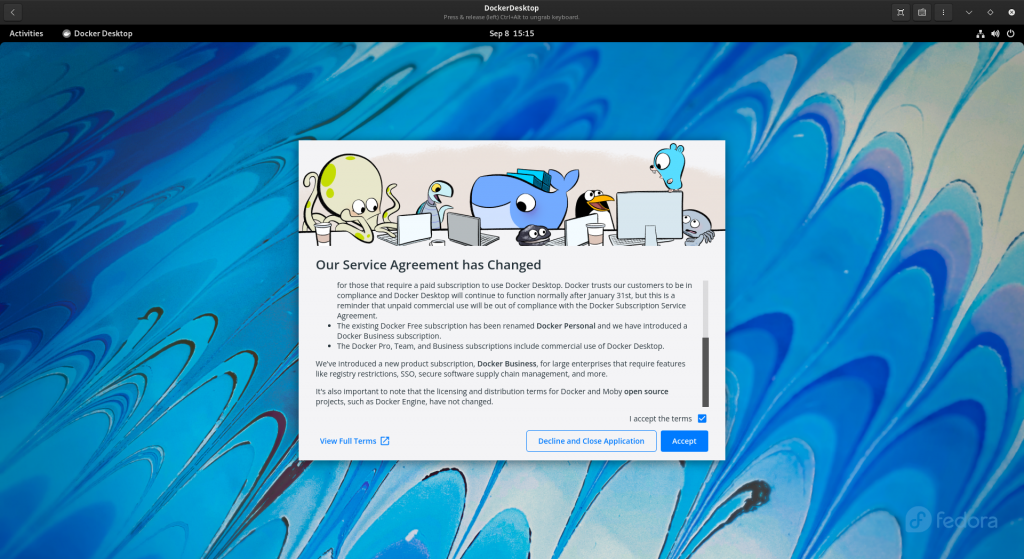
The first time you launch the Docker Desktop application you will get a pop up to accept the agreement. Read it and accept it if you are comfortable and launch the application.
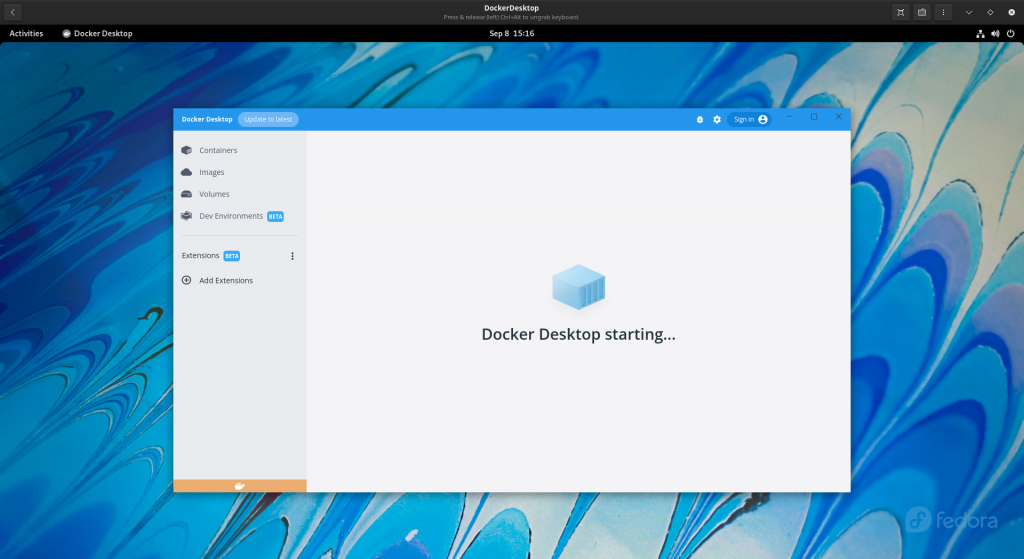
For the first it will show Docker Desktop Starting as shown below.
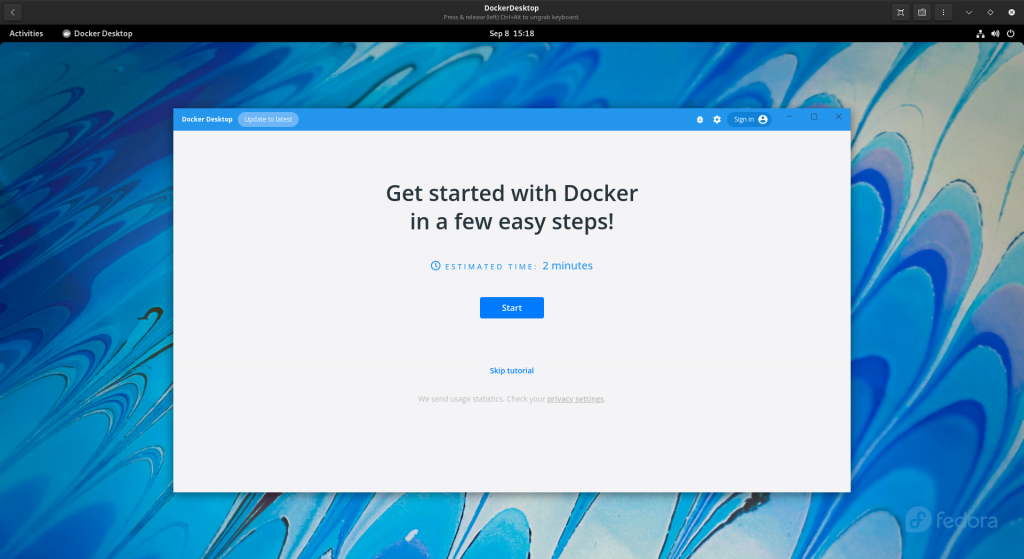
After a few minutes its ready to be used as shown below. You can follow the 2 min tutorial to experiment with Docker Desktop on how it works.
If you skip the tutorial you will get into the Docker Desktop Home Window where in you can manage your containers, images, volumes as shown in below screenshot.
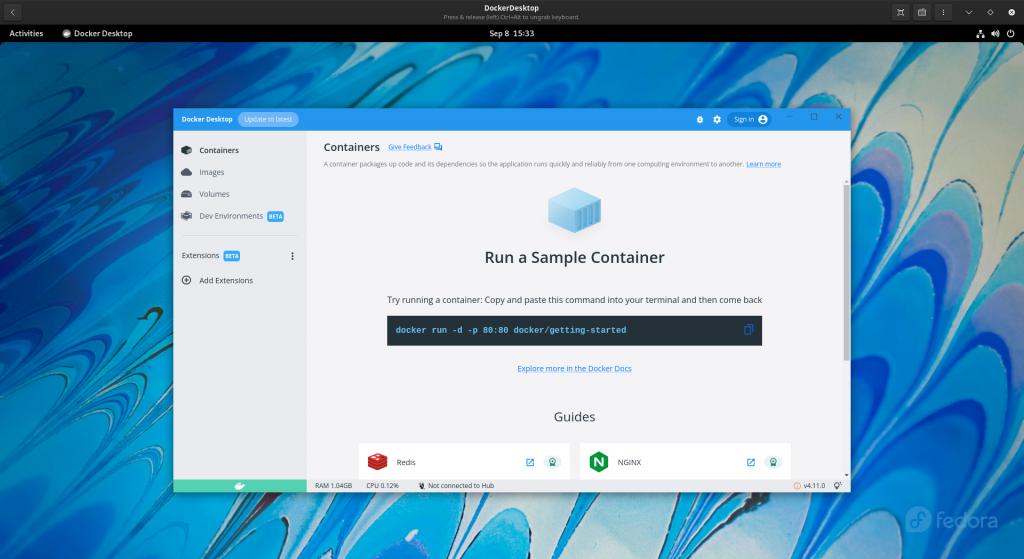
Hope you enjoyed reading this article. Thank you..
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.